
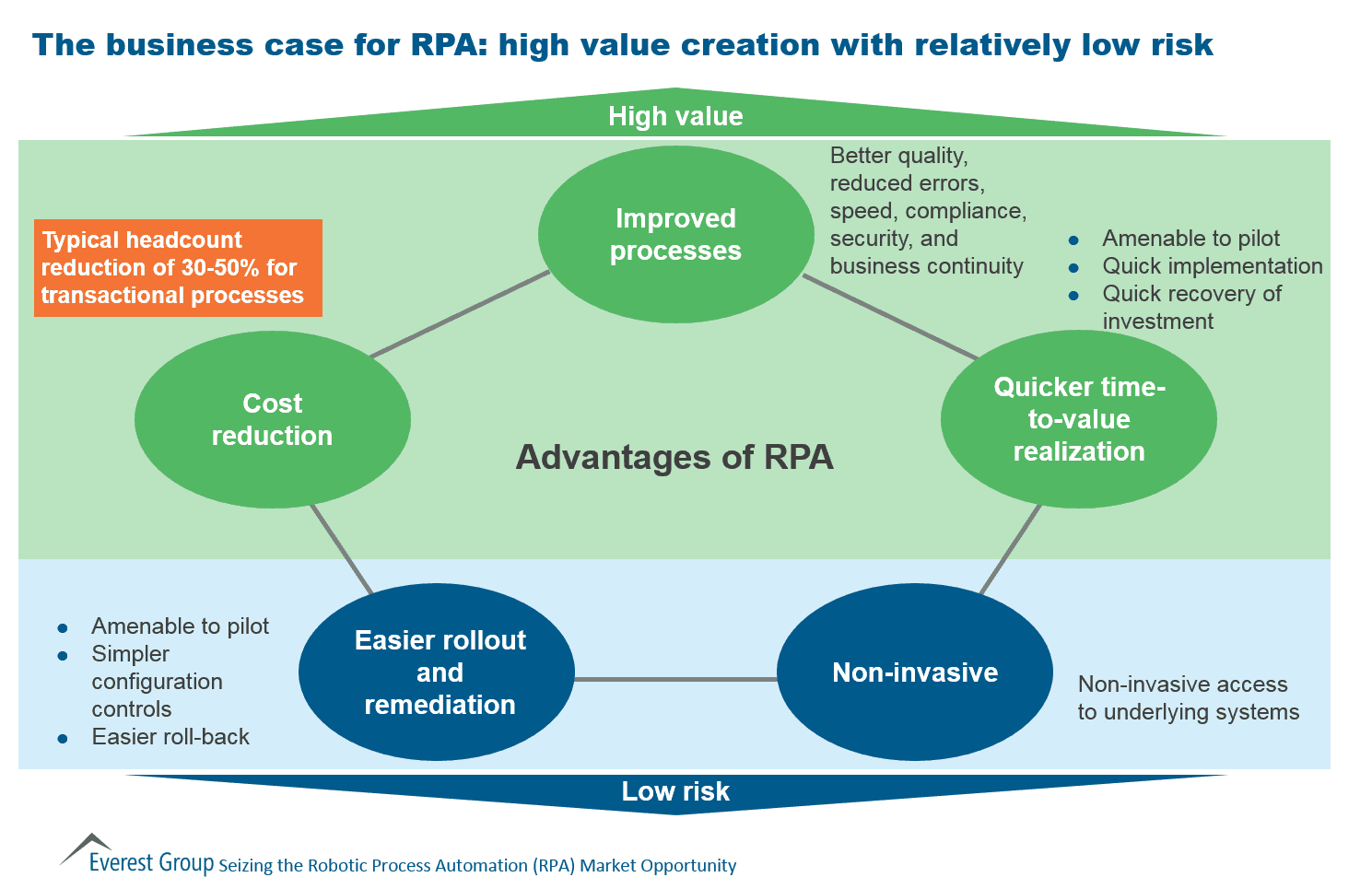
A bank deploys thousands of bots to automate manual high-volume data entry. Today, many major banks use RPA automation solutions to automate tasks, such as customer research, account opening, inquiry processing and anti-money laundering. More than 1 in 3 bots today are in the financial industry, which is of little surprise given banking's early adoption of automation. RPA implementations can be found across the following industries:īanking and financial services: In the Forrester report on “The RPA Services Market Will Grow To Reach USD 12 Billion By 2023”, 36% of all use cases were in the finance and accounting space. There are several industries that leverage RPA technology to streamline their business operations. A company must have 100 or more active working robots to qualify as an advanced program, but few RPA initiatives progress beyond the first 10 bots. According to a Forrester report, 52% of customers claim they struggle with scaling their RPA program. While RPA can perform multiple simultaneous operations, it can prove difficult to scale in an enterprise due to regulatory updates or internal changes. By educating your staff and investing in training programs, you can prepare teams for ongoing shifts in priorities. The adaptability of a workforce will be important for successful outcomes in automation and digital transformation projects. Organizations will need to promote a culture of learning and innovation as responsibilities within job roles shift. While RPA will reduce the need for certain job roles, it will also drive growth in new roles to tackle more complex tasks, enabling employees to focus on higher-level strategy and creative problem-solving.
Recompress rpa software#
While RPA software can help an enterprise grow, there are some obstacles, such as organizational culture, technical issues and scaling. To learn more about what’s required of business users to set up RPA tools, read on in our blog here. So, you can implement bots in situations where you don’t have an application programming interface (API) or the resources to develop deep integrations.
Less coding: RPA does not necessarily require a developer to configure drag-and-drop features in user interfaces make it easier to onboard non-technical staff.There are multiple benefits of RPA, including: RPA also enables AI insights to be actioned on more quickly instead of waiting on manual implementations. AI can help RPA automate tasks more fully and handle more complex use cases. That said, RPA and AI also complement each other well. While the use of artificial intelligence and RPA tools minimize the need for human intervention, the way in which they automate processes is different. Put differently, AI is intended to simulate human intelligence, while RPA is solely for replicating human-directed tasks. RPA bots can only follow the processes defined by an end user, while AI bots use machine learning to recognize patterns in data, in particular unstructured data, and learn over time. The critical difference is that RPA is process-driven, whereas AI is data-driven. AI combines cognitive automation, machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), reasoning, hypothesis generation and analysis. Robotic process automation is often mistaken for artificial intelligence (AI), but the two are distinctly different.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
